
Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It causes inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive system, leading to a range of symptoms and potential complications.
Here are some key points to understand about Crohn’s disease:
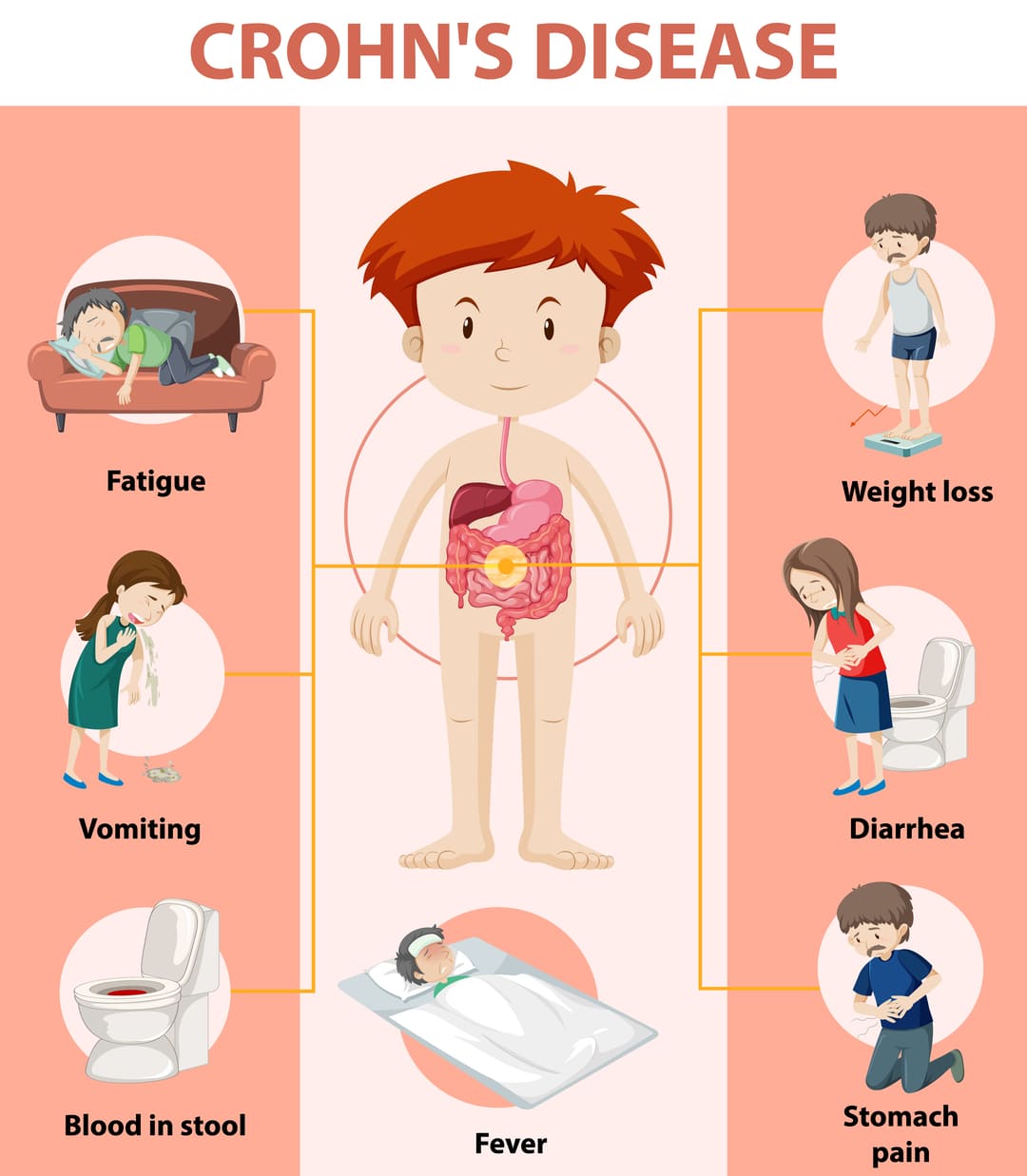
Symptoms: The symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary depending on the location and severity of inflammation. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhoea (often with blood or mucus), fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, fever, and rectal bleeding. Other symptoms may include joint pain, skin rashes, eye inflammation, or mouth ulcers.
Disease progression and types: Crohn’s disease typically follows a chronic and relapsing course, with periods of flare-ups and periods of remission.
It can affect different parts of the gastrointestinal tract, and several types of Crohn’s disease are recognized based on the location:
- Ileocolitis: Inflammation in the terminal ileum (the end of the small intestine) and the colon.
- Ileitis: Inflammation limited to the terminal ileum.
- Gastroduodenal Crohn’s disease: Inflammation in the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
- Jejunoileitis: Inflammation in the jejunum (middle part of the small intestine).
Causes: The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, but it is thought to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. A malfunctioning immune response is believed to trigger chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, potentially influenced by genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers, such as infections or lifestyle factors.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of Crohn’s disease involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies (such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, or imaging scans), and biopsy of the affected tissue. Differentiating Crohn’s disease from other conditions, such as ulcerative colitis or infections, is important for appropriate treatment planning.
Treatment: The goals of Crohn’s disease treatment are to control inflammation, reduce symptoms, achieve and maintain remission, and improve quality of life.
Treatment approaches may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs (such as aminosalicylates), corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologic therapies (such as anti-TNF agents) can be prescribed to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and suppress the immune response.
- Nutritional therapy: In some cases, a special liquid diet or nutritional supplementation may be used to help control inflammation and promote healing.
- Surgery: In cases where medication is not effective or complications arise, surgery may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve removing damaged portions of the intestine or repairing strictures, fistulas, or abscesses.

- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate hydration, can help manage symptoms and promote overall well-being.
- Monitoring and management: Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare professionals, such as gastroenterologists, are important to assess disease activity, adjust treatment as needed, monitor for potential complications or side effects of medications, and provide ongoing support.
- Support and self-care: Living with Crohn’s disease can be challenging, and support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or online communities can be helpful. Practising self-care, managing stress, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to treatment plans are important for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Treatments
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. The treatment of Crohn’s disease aims to control inflammation, manage symptoms, achieve and maintain remission, and improve the individual’s quality of life. The treatment plan for Crohn’s disease is tailored to…









